Inspection Methods of RMC: How to Ensure Your Chosen Concrete is Reliable?
Inspection Methods of RMC: How to Ensure Your Chosen Concrete is Reliable?
- February 23, 2022
- Posted by: Mir Ready-mix Concrete
- Category: General Construction, Ready Mix Concrete, Tips

No comfort in the world compares to the security of a home. Our species’ primary demand has always been a permanent roof over our heads. The journey that began with building their own shelters has engaged humans in creating infrastructures of all kinds for various purposes throughout the passage of time. During the last few decades, urbanization has increased the demand for infrastructural development by multiple folds. Therefore, the increased demand for concrete is not surprising given the massive expansion of construction work worldwide. Currently, concrete is even considered the world’s most used man-made substance.
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregates bonded together with cement paste that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is of different types, but ready mix concrete has surpassed all the other types of concrete in popularity due to its unique beneficial features. The ready-mix concrete industry is rapidly expanding to meet the rising customer demand. To fulfill consumer satisfaction and to avoid future construction hazards, assuring the highest quality of ready mix concrete is a significant task for any construction project.
Checklist
Testing and Inspection of Ready Mix Concrete
Quality control is a very crucial step in any type of construction because the stability of any infrastructure is dependent on the quality of the components used to construct it. Hence, before beginning any construction project, a thorough inspection is required to ensure the quality of ready-mix concrete. Inspection to ensure the highest quality of RMC begins by assuring that the materials are purchased from appropriate sources. The next steps involve sample verification and common quality assurance. All of the relevant tests’ reports must be double-checked for accuracy, followed by a comprehensive final inspection that may assist the customers in making the best decision for their project. Some common tests that may be performed to ensure the quality of RMC include:
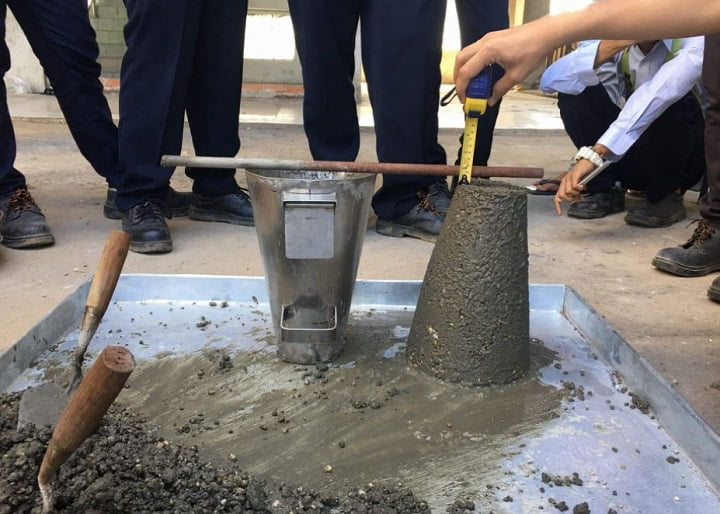
Slump test
After RMC has been manufactured, the slump test is the sole technique to check if the fresh concrete is of good quality for casting. The purpose of the slump test is to measure the workability of concrete. The consistency of ready mix concrete affects its workability the most; moist mixtures are more workable than drier mixes, but concrete of the same consistency can differ in workability. The slump test is also known as the relative fluidity of freshly mixed concrete. The test is carried out using a metal mold in the shape of a conical frustum known as a slump cone or Abrams cone that is open at both ends and has attached handles. After placing the cone on a hard, non-absorbent surface, it is filled with fresh concrete in three different stages. At the end of the third stage, the concrete is struck off flush with the top of the mold. To avoid disturbing the concrete cone, the mold is carefully hoisted vertically upwards, after which the concrete subsides at the bottom surface. The distance from the top of the slumped concrete to the level of the top of the slump cone is measured to determine the slump of the concrete.

Air content test
The air content test is carried out for detecting air entrainment within concrete after a new batch of RMC has been manufactured. Air content testing measures the overall air content in a sample of fresh concrete but does not show what the final in-place content is. This happens because a certain amount of air is lost during transportation, consolidating, placing, and finishing. For this testing purpose, the pressure method (ASTM C231) is widely preferred. This method determines the amount of air in fresh concrete of normal density. This method is more popular than other available methods due to being relatively faster.
Setting time
Setting time is another crucial characteristic to be checked for quality assurance of ready mix concrete. The concrete setting is defined by ASTM C125 as “the process, due to chemical reactions, occurring after the addition of mixing water, that results in a gradual development of rigidity of a cementitious mixture.” In simple words, the setting-time of ready mix concrete indicates the time required for solidifying concrete from a fluid state. In the concrete setting process, there are two critical moments:
- Initial setting time: The time when ready mix concrete starts to lose its flexibility indicates the initial setting time. At this point, the fluid mixture of concrete will begin to thicken and become difficult to manage.
- Final setting time: The time it takes for the concrete mixture to solidify is known as the final setting time. The concrete mixture can now keep a shape, and attempting to change it will compromise its strength.
Knowing how long concrete takes to set serves a useful purpose. For starters, the first setting time indicates how long it will take for the hardening process to begin after the water has been combined. As a result, before bringing RMC to the construction site, concrete mixing can be arranged according to the initial setting time for optimum results. At the same time, consolidating actions beyond the final setting time is not suggested since they will disrupt the concrete’s strength development. Both of the set periods should, in theory, be long enough to perform the job but not so long that the project’s development is hindered.
Compressive strength test
Compressive strength refers to the material’s or structure’s ability to support the weight of loads on its surface without any crack or deflection. When a material is compressed, it tends to shrink, and when it is stretched, the size elongates. The compressive strength test provides an overall idea of all the characteristics of ready mix concrete. So, it is undoubtedly a very significant test for inspecting the quality of RMC.
The compressive strength of ready mix concrete depends on many factors such as water-cement ratio, cement strength, quality of concrete material, quality control during the production of concrete, etc. The standard specimen for the test is usually a concrete cylinder or a concrete cube, according to various standard codes. Theoretical compressive strength testing associated with a specific water-cement ratio can only be achieved if the actual amount of water applied is precisely controlled. To verify whether compressive strength was actually achieved, samples (cube/cylinder) cast from the mix must be cured and examined. After 7, 14, 28, 60, and so on days of curing, a specialized machine is used to do this test.
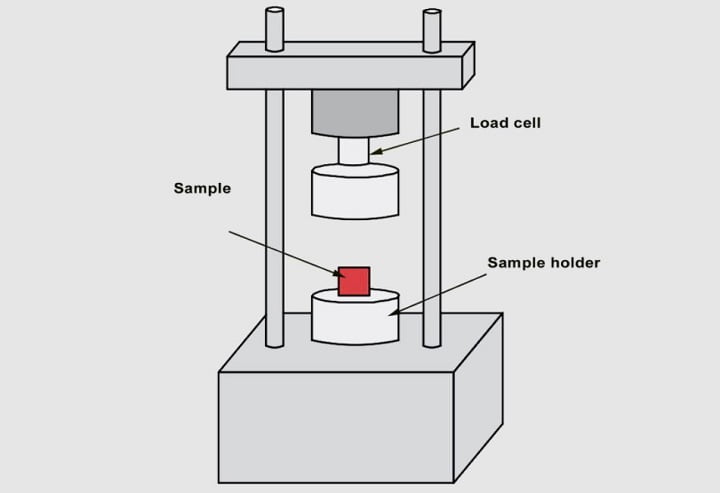
Tensile strength
Ready-mix concrete, as a substance, shows good performance while under compression but weaker performance in tension force. One of the most basic and crucial qualities of concrete is its tensile strength, which has a significant impact on the degree and size of cracking in structures. Concrete’s structure includes an ‘interface transition zone’ which is the weakest link present. When tensile stresses arise, the aggregates of concrete tend to separate from one another. Therefore, the interfacial transition zone must bear tensile loads to keep the whole system together. As this zone is weaker than aggregates, failure starts at much lower stresses. Moreover, it is unlikely to withstand direct tension. As a result, when tensile pressure exceeds the concrete’s tensile strength, cracks appear. So, the tensile strength of concrete must be determined in order to establish the load at which the concrete may crack.
The tensile strength of ready mix concrete is tested by the split cylinder test of concrete and it is measured by the units of ‘force per cross-sectional area’ (N/Sq.mm. or Mpa). In this test, a concrete cylinder specimen is placed horizontally between loading surfaces and loaded along its diameter. This loading results in producing lateral tensile stress in the cylinder and it splits in tension along its diameter.
Water permeability test
Water permeability of ready mix concrete determines the true resistance of concrete against the penetration of water under hydrostatic pressure. It is one of the most accurate ways of testing the durability of RMC as water permeability acts as a good indicator of that feature. Under hydrostatic pressure, the natural tendency of concrete to crack is thoroughly examined in accordance with the German Standard DIN 1048. This kind of test samples will be taken from substructures or concrete elements like foundations, concrete water tanks, retaining walls, etc. Concrete specimens are cast and cured for 28 days. After such time, samples are placed in the test device where they are subjected to hydrostatic pressure for three consecutive days. They are removed from the apparatus after three days and cracked vertically to evaluate the depth of water penetration. The lesser the penetration depth, the greater the resistance to water pressure.
Modulus of elasticity
The ratio of the applied stress to the corresponding strain is known as the concrete’s modulus of elasticity (Ec). It demonstrates not just ready mix concrete’s ability to tolerate deformation owing to applied stress, but also its stiffness. In other words, it reflects concrete’s elastic deflection ability. Ready-mix concrete’s modulus of elasticity is affected by aggregate and mixture quantities.
The accurate value of concrete’s modulus of elasticity can be determined by conducting a laboratory test called compression test on a cylindrical concrete specimen. In the test, the deformation of the specimen with respect to different load variations is analyzed. The average modulus of elasticity is calculated using the data acquired from the analysis, which is plotted on a graph.
Rapid chloride-ion penetration test
Rapid chloride permeability test (RCPT) is one of the widely used test methods to thoroughly detect the durability of RMC. This test is done specifically to determine ready mix concrete’s resistance against chloride ion penetrability. The most common cause of reinforcing bar corrosion is chloride ions from road salts or seawater. Corrosion reactions are aided by chlorides, which act as catalysts. Water, on the other hand, is required for the chlorides to migrate in and for the reactions to occur. Similar to the water permeability test, this is one of the tests used to measure the strength of concrete. For this test, three cubes of fresh concrete placed on-site will be taken and tested after 28 days. The test must be carried out according to ASTM C1202-97. This test method determines the electrical conductance of concrete to provide a rapid indication of its resistance to the penetration of chloride ions.
Initial surface absorption test
The Initial Surface Absorption Test (ISAT), as described in BS 1881 part 5, is designed as a laboratory method of determining concrete porosity. For quality assurance of RMC, this test is necessary for examining the absorption of surface materials. When the test is performed on-site, the results are heavily influenced by the current moisture conditions as well as the cleanliness of the surface. Waterflow into the test specimen through a known surface area is measured in this test. A plastic cell adhered to the surface defines the contact region. The volume of the flow is determined by measuring the length of the flow down a capillary of defined dimensions. The measured volume of the flow indicates the surface absorption rate of RMC.
In situ test on RMC
In situ testing on RMC is done to determine strength, durability, and the rate of deterioration. Also, to assess concrete’s durability, or its capacity to withstand the effects of service conditions such as loading, weathering, chemical attack, and abrasion, in situ tests are done. In-situ testing can virtually be divided into three groups, depending on the amount of destruction that will happen to the concerned structure when performing specific in situ tests. These groups are:
– Non-destructive tests
– Semi-destructive tests
– Destructive tests
Summary
Due to the intricacies involved, selecting an RMC product can be a difficult challenge. There are numerous approaches for determining the degree of concrete quality. Ready-mix concrete firms are required by law to have test facilities on their sites in order to undertake periodical tests such as concrete slump testing, concrete cube testing, and other tests to ensure the workability and strength of the ordered product. So, by being aware of all the tests and having inspection reports, and double-checking them, you can select the best ready-mix concrete for your project with ease.
F.A.Q.
What are some factors to consider before purchasing ready-mix concrete?
Ans: To know about some essential factors to keep in mind while buying ready-mix concrete, please follow this detailed guideline.
Why should you inspect the quality of ready mix concrete before buying?
Ans: The quality of the concrete used to construct your home must be verified to ensure its strength and stability. Quality assurance is also required to avoid accidents and deterioration of the infrastructure in the future.
How to ensure the workability of the ready mix concrete?
Ans: The concrete slump test and compressive strength tests can ensure the workability of ready-mix concrete. So before purchasing, you must check the reports of these tests or consult an expert to help you understand them if difficulties arise.
Which tests can ensure the durability of ready mix concrete?
Ans: The durability of ready mix concrete can be determined by tests such as water permeability test, rapid chloride-ion penetration test, initial absorption test, etc.
Where to find facilities to carry out the concrete inspection?
Ans: Usually, the concrete suppliers are bound by laws to have quality control facilities on their premises. So, contact your supplier if you are interested to inspect the quality of your concrete.
